What is new in the SNIP 3_17_00 release – released December 12th, 2024
(updating the prior release of 3_16_00 issued on October 9th, 2024)
This is the next production release of SNIP following the Rev 3_16 release. This release contains both major and minor improvements in response to user requests. This release supports both 32-bit and 64-bit installations on all Windows Platforms from Windows 7 to the current editions.
It is recommended that all Windows SNIP installations now update to using this release.
Changes in this release include
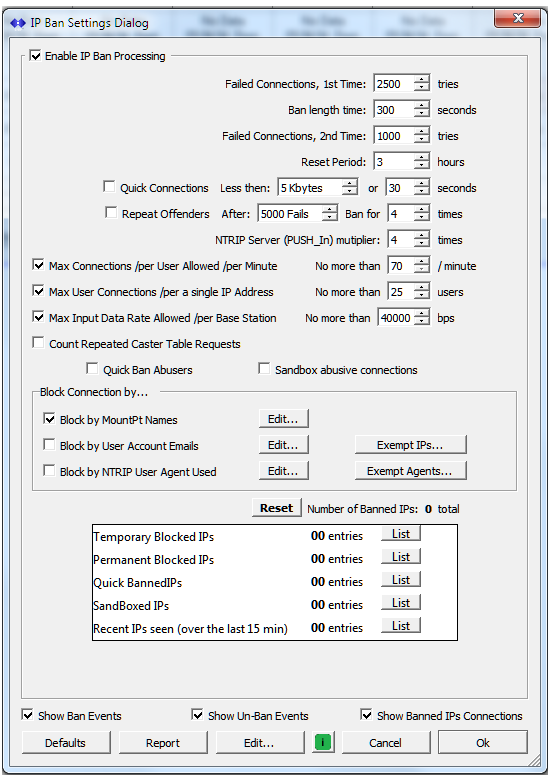
IP Ban and Blocking Logic Improvements
A new control has been added that allows blocking specific NTRIP Clients based on matching a full or partial text string to the NTRIP Agent string which they use (this is generally the product name and model being used).
The control used for blocking specific emails in the user account names has been reworked to make it easier to block an entire domain name.
The layout of the IP blocking dialog has been reworked to reflect a better grouping of the various controls. A knowledge base article on the general use of IP blocking and the various control can be found here.
NEAR Stream Improvements
The functionality of the Verbose checkbox in the NEAR Stream tab has been reworked and significantly increased. When checked, it now shows additional helpful information about the process of accepting or rejecting streams for the active NEAR pools. For example, if a stream is not used in a given NEAR pool, the reason for this is now shown in the console logs. Use this feature when debugging your NEAR streams. This checkbox always defaults to unchecked when SNIP is re-started, because it can produce large console logs.
As a side effect of the improved filtering process for broadcast orbital messages (see PFAT below), the NEAR logic used to include or exclude a given base station stream was revised to ignore both the presence or the filtering of ephemeris messages when considering a given stream for use in a NEAR pool.
Web API Improvements
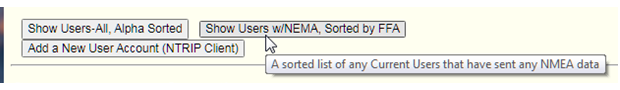
Improvements were made to the security model for the Web API when used by Customer Accounts. In the User account section are two buttons which can be used get a report of:
- All connected users (with or without NMEA and sorted alphabetically), and
- All connected users that have sent in a NMEA position (sorted by their Fix-Float state)
For the administrators (or any admin staff accounts) these buttons show all users regardless of any customer ownership. When these button where displayed to a customer account (or to the staff of a customer account) they were showing users who were not owned by that customer. This was a security leak and has now been corrected. Only the user accounts owned by the customer are shown. If the customer has no such user accounts, the section is not displayed.
In a similar fashion, if the customer account does not have ownership of any base stations, the sections shown in the top level web page which pertain to managing base stations are not displayed. This produces a much simpler top level page for some customer accounts.
Some additional connection details are now provided in the console log whenever a Web API login attempt fails in order to help the deployment operator with the debugging process.
P.F.A.T. Tool Improvements
In the editing of base station ID details the new ID value was not always being correctly saved. This has been corrected.
A new control has been added to the ECEF Base Station Adjustment dialog to control how often the messages MT1005 and MT1006 can be sent. This control provides an easy method to limit sending these message when it is needed. This article describes its use in more detail.
The PFAT Filter dialog has be revised to add a new control to easily filter out all the Broadcast Orbital messages (the ephemeris messages) in a base station data stream. This article describes its use in more detail.
Miscellaneous Improvements
Minor changes were made in the run time scheduling algorithms used to run background processes in SNIP. The new system uses an adaptive scheduling approach where some slow periodic tasks are delayed for as much as tens of seconds whenever the Caster is heavily loaded with transitory new client connections. A “catch up” run is then performed (and noted in the console logs).
The run time clock displayed at the bottom of the SNIP window now updates every 1~2 seconds. And the display of the seconds is now shown after SNIP has been operational for greater than 24 hours (in prior releases only the minute was shown after the first day or operation). This was done based on customer feedback that the additional information provided a level of comfort to the operator.
The Google map API has been updated to use release 3.55
A few dialog windows were widened to accommodate font and GUI control placement issues seen in some regional deployments of SNIP that are running Windows 11.
How to Update…
Updates to SNIP are always free and easy. Your Caster will be offline about 3 minutes. From within SNIP, simply use the menu item Help ⇒ Check for Updates… Your update will be downloaded from our secure servers. Then you will be asked to allow SNIP to restart and update itself. On some Windows 10 and 11 systems you must also manually exit the current copy of SNIP to complete the update. It takes about three minutes to do and have your Caster back on-line. That’s all there is to it!