What is new in the SNIP 3_07_00 release – released November 3rd, 2022
(updating the prior release of 3_06 issued on August 16th 2022)
This is the next production release of SNIP following the Rev 3_06 release. This release contains both additional features added to the Web API commands, and new types of User Restrictions, as well as various minor improvements in response to user requests.
This release supports both 32-bit and 64-bit installations on all Windows Platforms from Windows 7 to the current editions. It is recommended that all Windows 32/64 SNIP installations now update to using this release.
Changes in this release include
New Web API Commands
Four new commands have been added to the Web API Top Page.
Display All Connected Users
This Web API command provides a sorted list of the currently connected users very similar to the report from the SNIP menu report: Reports ⇒ Active Users ⇒ By Name. The list is sorted by the Base Station to which each user is currently connected. [To see a list sorted by the User Account names using the Web API, press the Search button. To see the connected users from the console, use the Display Current Users menu item] The report contains extensive hyperlinks to other details including an individual User Account report, a report about the IP it connected with, and a Base Station report. See the article Web API, Display All Connected Users for additional details.
Display Connect Users by Fixed / Float State
This Web API command provides a sorted list of the currently connected users which have provided any NMEA $GGA information. It is sorted by the reported RTK status (into Fixed, Float, or Anonymous/Other). In addition, a new report has also been added to the SNIP menu reports under: Reports ⇒ Active Users ⇒ By Fixed / Float / Anon. This report contains extensive hyperlinks to other details including an individual User Account report, a report about the IP it connected with, and a Base Station report. See the article Web API, Display Users by Fixed / Float State for additional details.
Display IPs by most used
This Web API command provides the same information as the SNIP menu report: Reports ⇒ Network Traffic ⇒ IP Usage Report. It provides a summary of the IPs most frequently connecting to the Caster. See the article IP Most-Used Report for additional details.
Display Banned IPs
This Web API command provides the same information as the SNIP menu report: Reports ⇒ Network Traffic ⇒ IP Bans Report. It provides a summary of all currently banned / blocked IPs on the Caster. See the article IP Blocked Report for additional details.
A bug was corrected in the Create New User Account Web page where the new user password was not being saved.
By request, the most recent console log reports are now available for read-only Web API users as well as read-write users.
New User Account Restrictions
Two new User Account Restriction methods have been added:
By Geographical Region
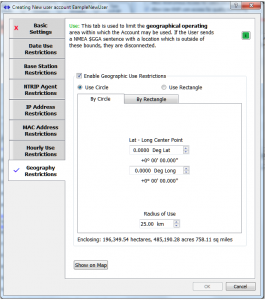 This restriction allows controlling where an individual User Account must be located in order to connect to and use the Caster. Use it to create a Geo-Fence for a user.
This restriction allows controlling where an individual User Account must be located in order to connect to and use the Caster. Use it to create a Geo-Fence for a user.
A circular or rectangular region can be set up as desired. When a user with this restriction connects, if they are outside of the region the connection is dropped. When such a user moves outside the allowed region, the connection is dropped. Users within their assigned regions connect and operate normally.
The details are described further in the article Restricting Users, with a Geo-Fence.
By Usage Time
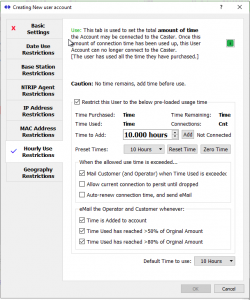 This restriction allows controlling the amount of time an individual User Account can be connected to the Caster. Use it when you wish to meter the overall Caster connection time for a user.
This restriction allows controlling the amount of time an individual User Account can be connected to the Caster. Use it when you wish to meter the overall Caster connection time for a user.
With this restriction, individual User Accounts can ‘purchase’ connection time in units of hours. As the connection time is used up (accumulated) a variety of warning eMails can automatically be sent to the account owner (the customer) and to the Caster operator. When the allocated connection time is exhausted, a variety of options can occur including disconnecting the user, extending the time, or auto-renewing the account with additional connection time. User Accounts which have exhausted their time are not allowed to connect until more time is added.
The details are described further in the article Restricting Users, by Hourly Use.
NEAR Stream Improvements
Any streams placed in the “not used” pool are now periodically resorted, this occurs every 5 minutes. This change was promoted by some base stations which periodically changed the IP used to connect to the Caster causing the data stream to be mangled during that time. With this change, they are again used in the NEAR stream once they are stable.
NEAR Streams can now be added and used in the User Account By-Base restrictions. In prior editions only physical Base Stations could be added to the lists of stations a User Account could use or not use.
And, when a connected User Account with a Base Station restriction to a NEAR stream changes to another base (due to the user’s reported NMEA location) the new station is also checked to confirm that user is allowed to access it. These changes support the following requested use case: Consider a Caster which has been set up to show only a NEAR stream with all other Bases set as hidden. The operator wants to allow a given User Account to connect by way of the NEAR stream, but then only to be able to use (connect to) a specific set (one or more) of the Bases that are present. By listing the NEAR stream and the bases they can connect to in the By-Base restriction, this is accomplished. See the article Restricting Users, by Base for further details.
IP Blocking and Related
Some new logic called Quick Ban allows effectively blocking problem connections after the first attempt (rather than waiting for the bad connection to repeat to the number of times set in the IP blocking dialog threshold). This is of value in two common use cases: First, when a connection is so obviously incorrect there is no point in allowing it to repeat further, and second, when an ill-formed connection is changing the IP it uses with every new connection.
Web Bots seeking to get a list of all the article authors from your Caster (they are presuming your NTRIP Caster is a WordPress site) are now detected and banned.
Devices that connect and then present initially huge message loads are detected and Quick Banned.
Devices that connect without ever sending any proper NTRIP Header and then send NMEA or RTCM3 (or other selected content) are also Quick Banned. Aside: If you have an older Base Station device that does not speak NTRIP, use the Raw TCP/IP tab to allow these devices to connect.
Misc. Improvements and Changes
Internally a unique ID is now assigned to every Base station (data stream) when first created to allow the correct tracking of that stream when/if the operator edits the public name to be used for the stream. This is only a problem when multiple data streams share the same name (NTRIP requires that every data stream have a unique public name, and SNIP provides a number of methods to ensure this occurs).
The logic that creates the ‘NET’ Caster stream entry used in the Caster Table has been updated. This overcomes a potential problem with Caster naming when running multiple Casters (a Plug-In feature) on different ports or IPs
The file data path set by the operator where various logs, reports, backups, and base station raw observation files are kept is now respected and used correctly. This is set up in the Log Settings dialog box. In prior versions some files would not correctly use the path which the operator had entered. And, any change in the file path was not used everywhere until the SNIP application was restarted.
Some reports dealing with banned connections showed the total number of lifetime bad connections as zero whenever the user reached the threshold for bad connections in a row and was blocked. This has been corrected to display the correct count.
In the Caster table entries, SNIP now detects when an entry is incorrectly stating zero as the number of carriers present and automatically corrects this (typically to the value ‘2’ when L1 and L2 carriers are present). This minor change greatly helps some older Trimble devices that depend on this value being correct.
In the Connected Users dialog, the NMEA fix state (fix/float/anon) is now displayed in a new column before the NMEA count and NMEA Age columns. Like other columns, this is sort-able when you click on the header.
The very aggressive back off timer interval seen for Remote-Relay secure TLS/SSL connections which occurred when the connection failed to connect, has now been corrected.