SNIP supports Geographic Reverse IP look-ups for the IP connections used by NTRIP Client users and for GNSS Base Station devices.
How it works
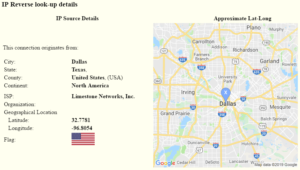
Whenever a device with a new IP value connects to a SNIP Caster, it is added to SNIP‘s cache for logging and tracking. With Geographic Reverse IP look-ups some addition basic information about the source is also provided, as shown below.
Where is it Used
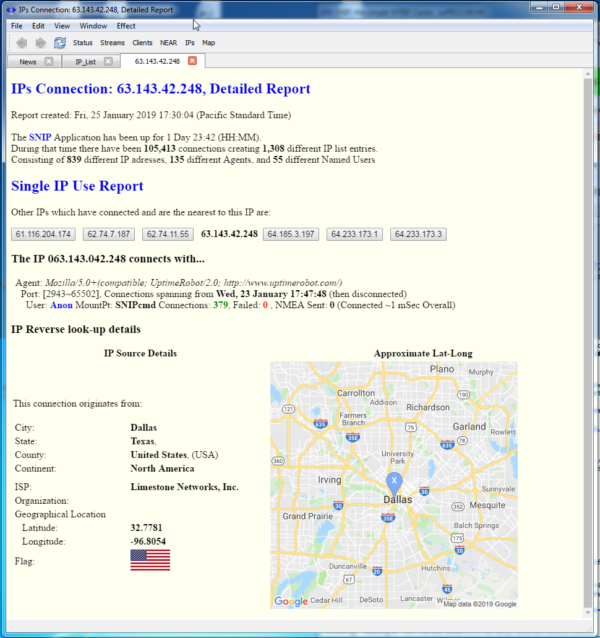
The resulting information is typically used along with a general report about a single IP address and how it has connected to SNIP. This is found in the “Single IP Use Report” that is accessed by clicking on the links for any IP address in the main console log or in any of the document viewer reports. Here is a typical report, for the IP 63.143.42.248, where the Geographic Reverse IP look-up data is shown (click to enlarge).
 If Geographic Reverse IP look-ups are disabled (on Lite models of SNIP), then the two sections of the report are left blank.
If Geographic Reverse IP look-ups are disabled (on Lite models of SNIP), then the two sections of the report are left blank.
The report will also be blank when a “private” IP address is used such as those starting with “192.168.x.x” or with “10.x.x.x” – values in these ranges are not assigned to a specific ISP.
In the case shown at in this image, the IP is used by a 24/7 monitoring service (the user agent string ”uptimerrobot.com'” tells the reader that).
This IP has successfully connected to this SNIP Caster node 379 times over a span of about 2 days. And it is repeatedly asking for a status page (otherwise other entries would be present). The information in this section is a typical SNIP IP report. The connects with… section can be quite long and varied if the remote user is connecting to different Base Stations and/or using different types of software tools to do so.
The information below this (IP Reverse look-up details) informs us that this request came from the greater Dallas Texas area (USA), originating from an IP owned by a service provider called Limestone Networks. The small map at right serves to provide a quick context.
Note: A few words on the relative location accuracy of Reverse IP look-ups.
Reverse Geo-location taken from the IP is generally correct only to the City level (tens of km at best). At times it can be very very incorrect. The db used by SNIP is updated daily with new changes to track this. A further side effect of this is that multiple dispersed NTRIP Clients in the same general operating area may appear at the same ‘city center’ location, when in fact all that is known is that they share a common ISP operator. By contrast, the location values used by SNIP for Caster tables entries (~500m) or in Rover NMEA $GGA strings (~2m) or in the Base Station location (~mm) are all much more accurate. Map locations which are plotted by these methods are therefore of high confidence and much more accurate.
Arbitrary IP Lookup Feature
You can also use this feature in SNIP to look up any IP value you enter, even if that IP has never connected to your Caster. Select the menu item under Reports ⇒ Active Users ⇒ By IP Used … to bring up a dialog to enter any IP you wish to check. The combo list will also display all the IPs known to SNIP at that time along with tool tips about the stream contents which that IP is associated with.
Model Use and Plug-In Notes:
Note: The Geographic Reverse IP look-up feature of SNIP is a was planned to be Plug-In (which would require an annual subscription service). but is not 100% free to for all paid models (Basic and Pro). This changes the prior policy where the feature was free for Lite as well as all models and the end of use date was often updated during the past few years. To repeat, the Geographic Reverse IP look-up feature is being freely provided for all paid users and all models of SNIP, and will also operated when in the Evaluation mode for all new uses. [This change was made December 2022]