What is new in the SNIP 3_10_00 release – released June 05 2023
(updating the prior release of 3_09 issued on March 02 2023)
This is the next production release of SNIP following the Rev 3_09 release. This release contains both major and minor improvements in response to user requests. This release supports both 32-bit and 64-bit installations on all Windows Platforms from Windows 7 to the current editions.
It is STRONGLY recommended that all Windows 32/64 SNIP installations now update to using this release. You will not be able to use most Google Map features until you update to this release.
Changes in this release include
Map Displays
In recent months the Google map API that SNIP uses has been changing. In SNIP Rev 3.09 changes to the map software was required when Google dropped support for older map versions, forcing SNIP to move to Google API 3.x in that release. In mid-May Google dropped support for any map API before release 3.51 this again affected several basic map features, you can read more in this article. In the current Rev 3.10 release, all SNIP all maps are again working. But sure to update to this revision to restore map displays.
A few Map changes were also made to the Legend check box logic to enable / disable various display items which had ceased to function correctly. This is now working again, but the “cluster mapping” display which combined multiple push-pins when they were spaced closely tighter on the map has been disabled in this release.
The Preferences Dialog will now allow you to enter your own Google API key to be used. This is not a feature that the SNIP operator will generally need to use unless they are routinely creating a large number of maps. At this time, you can obtain your own keys from Goggle at no charge. A new test button has also been created to allow the operator to easily create a test map which can be used to validate that the entered key works.
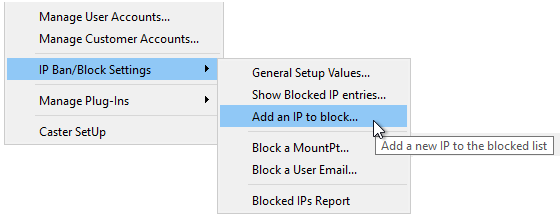
IP Bans and Blocking
The various component sections of the IP ban and blocking logic have now been split out into their own sub-menus, rather than accessing them from the primary IP Blocking dialog box. This provides a less modal experience when the operator needs direct access one element of the system (say to easily block an IP).
New logic for adaptive “quick bans” and for “sandboxing” bad connections has now been implemented. This can be used to manage various recurring bad connections where the users source IP changes. The process can be enabled or disabled with two new checkboxes in the general IP Blocking dialog box. These two approaches complement each other. The quick-ban logic detects certain ill-formed connection attempts and blocks the offending IP for ten minutes thereafter (rather than waiting for the event to occur hundreds of times in the row without success as other ban rules do). If the problem with that IP continues after the ten minutes, the block is renewed and the duration is increased by 20% each time it re-triggers. This continues until the offending IP no longer tries to connect incorrectly. The sandbox logic detects bad connections that are reconnecting more quickly than they should (often many times per second) and employs a different process than simply disconnecting the offending IP. In this case, the connection is not dropped, but nonsense data is feed back to the bad connection at a constant but slow rate. This continues until the offending IP no longer tries to connect incorrectly. These two new rules serve to handle the problem of bad NTRIP devices who connect using cellular DHCP methods where the source IP often changes. They provide a more robust solution than permanently banning specific IPs in either SNIP or the host machine firewall.
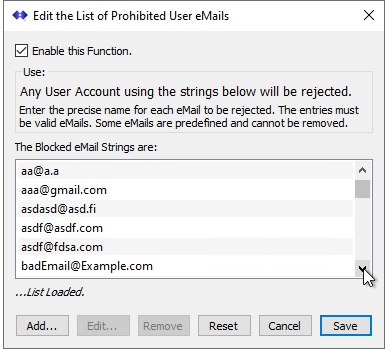
You now can also ban user connections (NTRIP Client connections) from specific email accounts. This is used when your Caster allows autonomous connections, but also requires that they provide a valid email. Some users will enter well-formed but fake emails (such as imaFake@gmail.com) which will then result in a bounced email posting when the connection fails (presuming the Caster has an active eMail Plug-In). An example of this dialog, which is very similar to the dialogs used for blocking specific mountPts names and for exempt IPs (IPs which are never to be blocked), is shown below.
Push-Is Base Station Streams
An automatic resorting feature has been added to the Push-In streams tab. When checked, this will periodically cause all the active Push-In streams to be re-sorted according to the setting last set in the Sort-By combo box. You can, for example, set the combo to sort by mountPt Name, then check this option. As new Push-In streams come and go, the display ordering would then remain alpha-sorted.
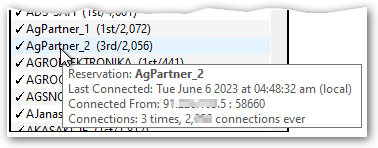
Push-In connections with reservations now log the last IP and port used to connect with. This new information is added to the tool tip along with the date of the last connection and some connection counts that has been displayed in prior editions of SNIP.
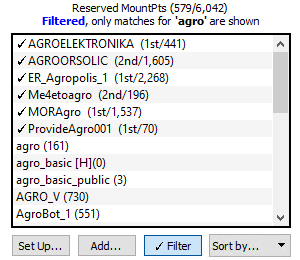
The list of Push-In reservations can now be filtered to show only a matching sub-set of the overall entries. This is of value when you have a great many entries and are seeking to find the one(s) that match. In the below image only entries that contain the string “agro” are shown. The string matching process is case insensitive. Pressing the Filter button a 2nd time removes the filter.
Customer Accounts
Customers can now be assigned ownership of ANY Base Station stream type, not just Push-In reservations as has been done in the past. Some deployments wanted to assign ownership to Remote-Relay streams, prompting this improvement. Reports about the customer account will also now include details about any of these assigned Bases. Details about the assigned bases can also be seen by the customer when using the Web API interface.
The logic to detect and resolve any indexing conflicts in base station and user account assignments for the customer account has been improved and should prevent any duplicate assignments from occurring.
A new checkbox labeled ”See General Reports” (in the Customer Edit Dialog) controls if the Customer is allowed to see and receive the general status report details for the Caster. You can disable or enable this in various reports for each specific customer to control if they are party to general details about the Caster operation. Be sure to also disable it in the general Preferences Dialog as well (which controls sending this information to the general user community by open web pages).
User Accounts
An import and export function has been added, see the article Import-Export User Accounts for further details. This allows exporting the current User Accounts (as well as various meta information about recent usage) into a tab separated text file. Operators can also import user accounts, useful when transferring from another Caster developer or creating bulk user accounts. A variety of import options are provided.
An error where the Print and Email buttons on the Edit User Account button did not work for all users has been corrected (email is an optional Plug-In feature).
Web API Tools
The keywords used for some API commands (such as Login) are now treated as case insensitive. This was done to aid Web API users with constrained keyboards (phone and tablet devices).
Misc. Improvements
The adaptive rate used for various Tool-tip updates has been reworked for larger deployments (those with 400 or more active Base Stations). This was done to further conserve processing MIPS. A new right-click menu item marked “Update Tooltip” is active and enabled when this is in use. Select the menu item to enable tips on that stream. For most deployments this menu it is disabled and the tips are always updated every few seconds.
The overall length of the console log is now increased proportionally to size of the deployment (number of allowed base stations). There is a proportional growth in the memory footprint to support this. But it allows displaying a longer console log spanning over days and hours, even on extremely busy Caster machines.
During times of extreme processor overloading, throttling of new connections now occurs. This most often occurs on host machines that are not dedicated to running the SNIP NTRIP Caster but have other applications running (such as WordPress). During short periods of overloading (often because another application has consumed all available processing resources), any new user connections are forced to wait a few seconds before being processed. This delay is typically inconsequential to the new user. All existing user connections, and base station connections, are not affected by this. An icon with a small “P” (for paused) is shown when this occurs. Most deployments will never see this.
At SNIP startup all the various streams and reservation are now cross-checked for any indexing assignment conflicts and other quality tests. If any are found, they are resolved before continuing the startup process. This test requires a one-to-one comparison with each entry (so for 100 bases it performs 10,000 tests) and can consume many seconds on larger deployments.
How to Update…
Updates to SNIP are always free and easy. Your Caster will be offline about 3 minutes. From within SNIP, simply use the menu item Help ⇒ Check for Updates… Your update will be downloaded from our secure servers and then you will be asked to allow SNIP to restart and update itself. On some Windows 10 systems you must also manually exit the current copy of SNIP to update. That’s all there is to it!